Finger Vein Technology
Accurate and counterfeit-proof authentication
is achieved with Finger Vein Recognition
The finger vein authentication technology developed by ETUNNEL
is a new technology with excellent security, versatility,and immunity to hacking.
ETUNNEL has filed global patents (in the US, Japan, Europe, South Korea, etc.) and
is currently being used by the Ministry of Defense, government offices, and various companies.
When logging into a computer, using an ATM, or passing through certain areas,
passwords and fingerprints are commonly used as methods of identity verification.
However, several issues with these methods have been pointed out.
Finger vein authentication technology is a relatively new method in the field of biometric authentication.
It works by verifying whether the finger vein pattern of an individual matches pre-registered data.
With its excellent security, it is replacing traditional methods such as passwords and fingerprints,
and is emerging as the best alternative to prevent hacking and cybercrime.
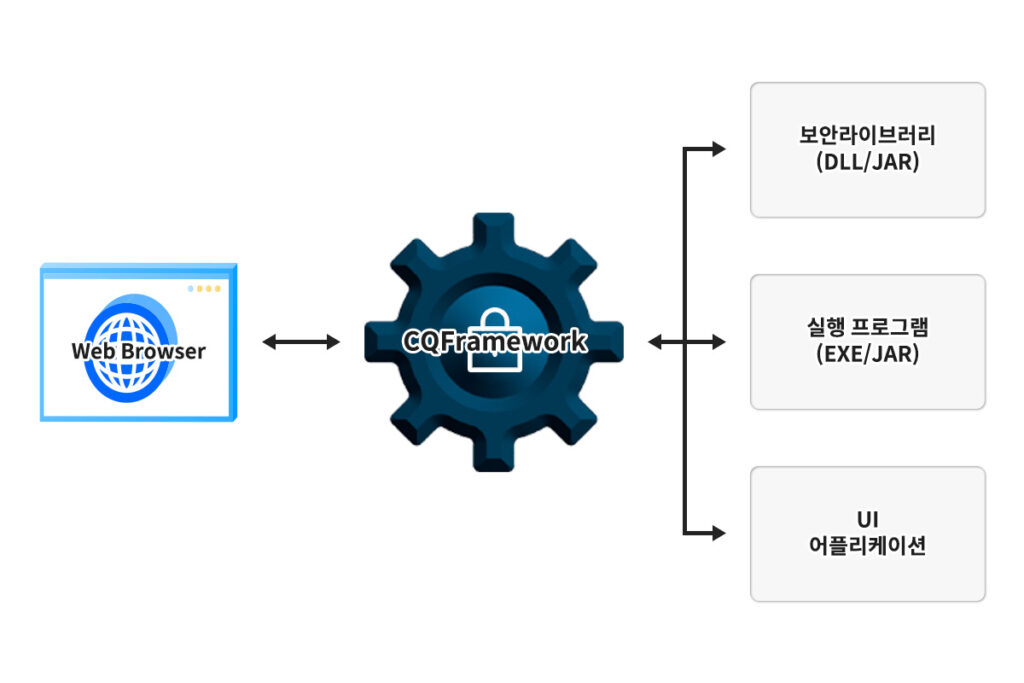
CQFramework는 웹브라우저와의 통신을 위해 자체적으로
localhost 통신 기능이 내장되어 있고 HTTP와 HTTPS를 모두 지원합니다.
CQFramework는 EXE와 JAR 2가지 형식으로 제공되어
다양한 환경에 적용할 수 있습니다.
How it works
Operating Principle
Near-Infrared (IR) Light Transmission
- A near-infrared (IR) light source illuminates the finger.
- Hemoglobin in the blood absorbs near-infrared light, allowing the detection of finger vein positions.
- The internal finger vein pattern is analyzed by distinguishing areas that absorb light (darker regions) from areas where light passes through (brighter regions).
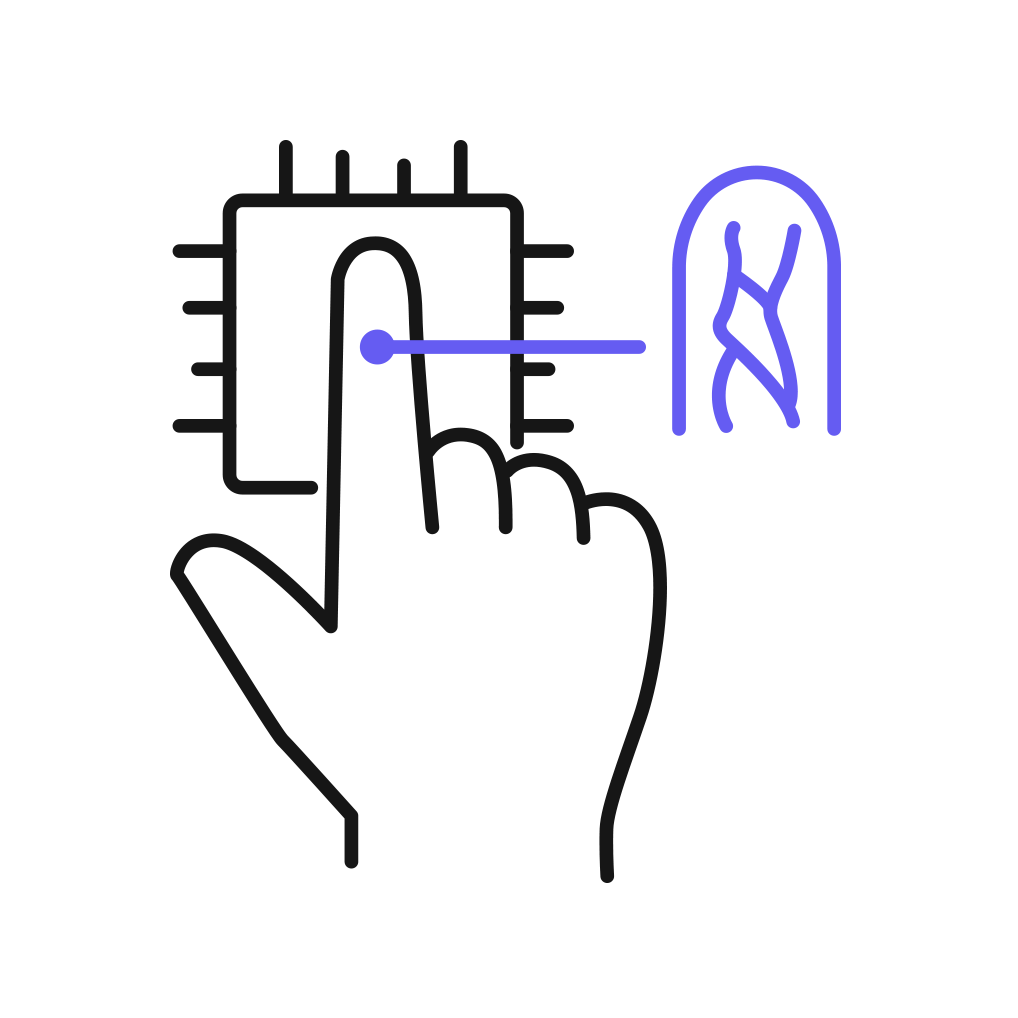
Finger vein Pattern Image Generation
- Specialized sensors capture and convert finger vein patterns into images.
- The captured images are transformed into unique biometric data and securely stored in an encrypted format.
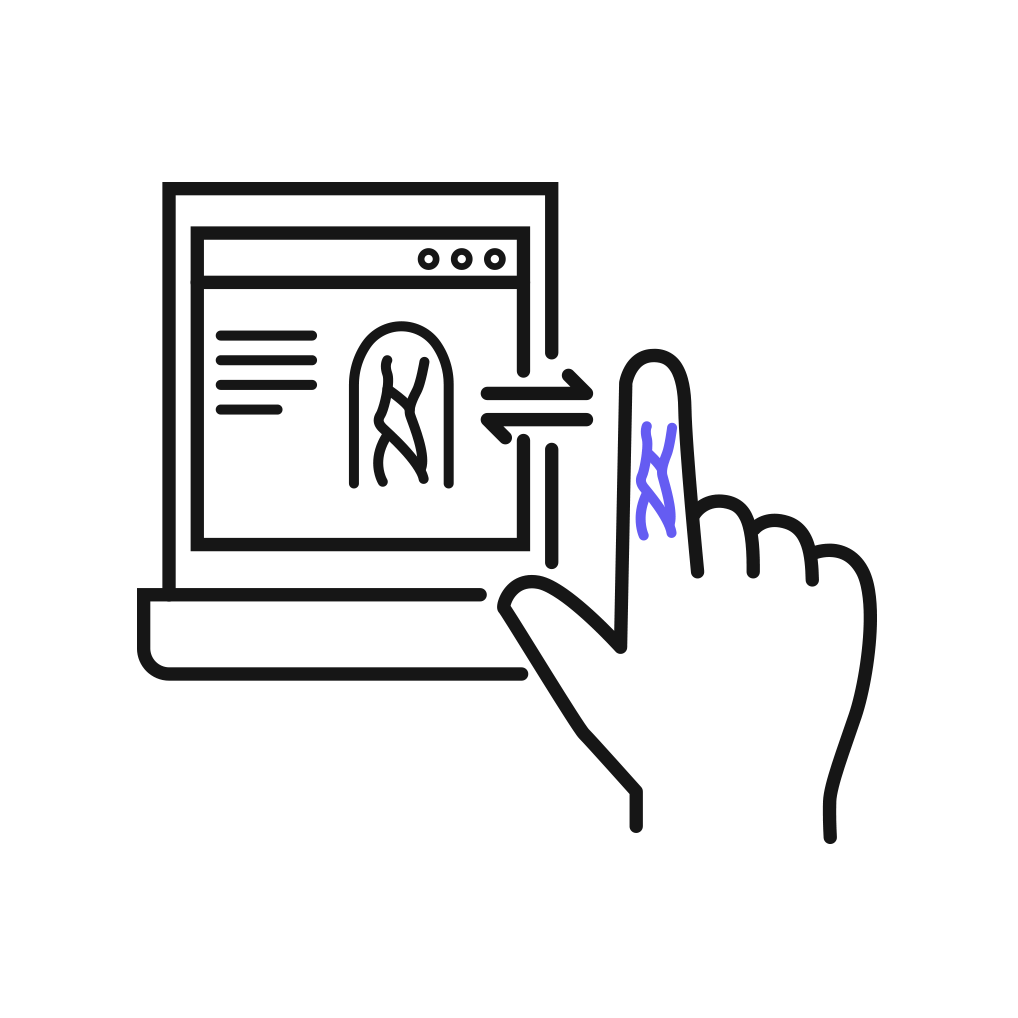

Data Comparison and Authentication
- During authentication, the newly captured finger vein pattern is compared against the pre-registered pattern data to determine a match.

Near-Infrared (IR) Light Transmission
- A near-infrared (IR) light source illuminates the finger.
- Hemoglobin in the blood absorbs near-infrared light,
allowing the detection of finger vein positions.
- The internal finger vein pattern is analyzed by
distinguishing areas that absorb light (darker regions)
from areas where light passes through (brighter regions).

Finger vein Pattern Image Generation
- Specialized sensors capture and convert finger vein patterns
into images.
- The captured images are transformed into unique biometric
data and securely stored in an encrypted format.

Data Comparison and Authentication
- During authentication, the newly captured finger vein pattern is compared against the pre-registered pattern data to determine a match.

Near-Infrared (IR) Light Transmission
- A near-infrared (IR) light source illuminates the finger.
- Hemoglobin in the blood absorbs near-infrared light,
allowing the detection of finger vein positions.
- The internal finger vein pattern is analyzed by
distinguishing areas that absorb light (darker regions)
from areas where light passes through (brighter regions).

Finger vein Pattern Image Generation
- Specialized sensors capture and convert finger vein patterns
into images.
- The captured images are transformed into unique biometric
data and securely stored in an encrypted format.

Data Comparison and Authentication
- During authentication, the newly captured finger vein pattern is compared against the pre-registered pattern data to determine a match.
Features of Technology
Discover the key advantages of
finger vein authentication — safer than fingerprints and more accurate than facial recognition.
Uniqueness
Finger vein patterns are unique to each individual, even among identical twins. This ensures a high level of security.
Fast Authentication Speed
The authentication process is completed within one second, enabling real-time authentication.
Anti-Spoofing Protection
Finger vein patterns are based on subcutaneous blood vessel structures, making
them difficult to replicate or forge externally.
This results in lower susceptibility to spoofing
compared to fingerprint or facial recognition.
Biological Response Verification
The system verifies whether blood is actively flowing (detecting blood circulation) to prevent authentication attempts using artificial models or deceased individuals.
Resistance to External Environmental Factors
Since veins are located beneath the skin, they are minimally affected by external environmental conditions such as humidity, temperature, and dust, as well as surface conditions of the hand, including cuts, sweat, or oil.
High Durability of Authentication Area
Since veins are not affected by external damage (e.g., fingerprint wear or facial wrinkles), long-term authentication accuracy is maintained. The system is also resistant to issues caused by sweat or oil.
High Accuracy
The authentication process is fast, with low false rejection rates (FRR) and false acceptance rates (FAR), ensuring high reliability.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Finger vein authentication can be integrated with other security measures such as passwords and RFID to enhance overall security levels.
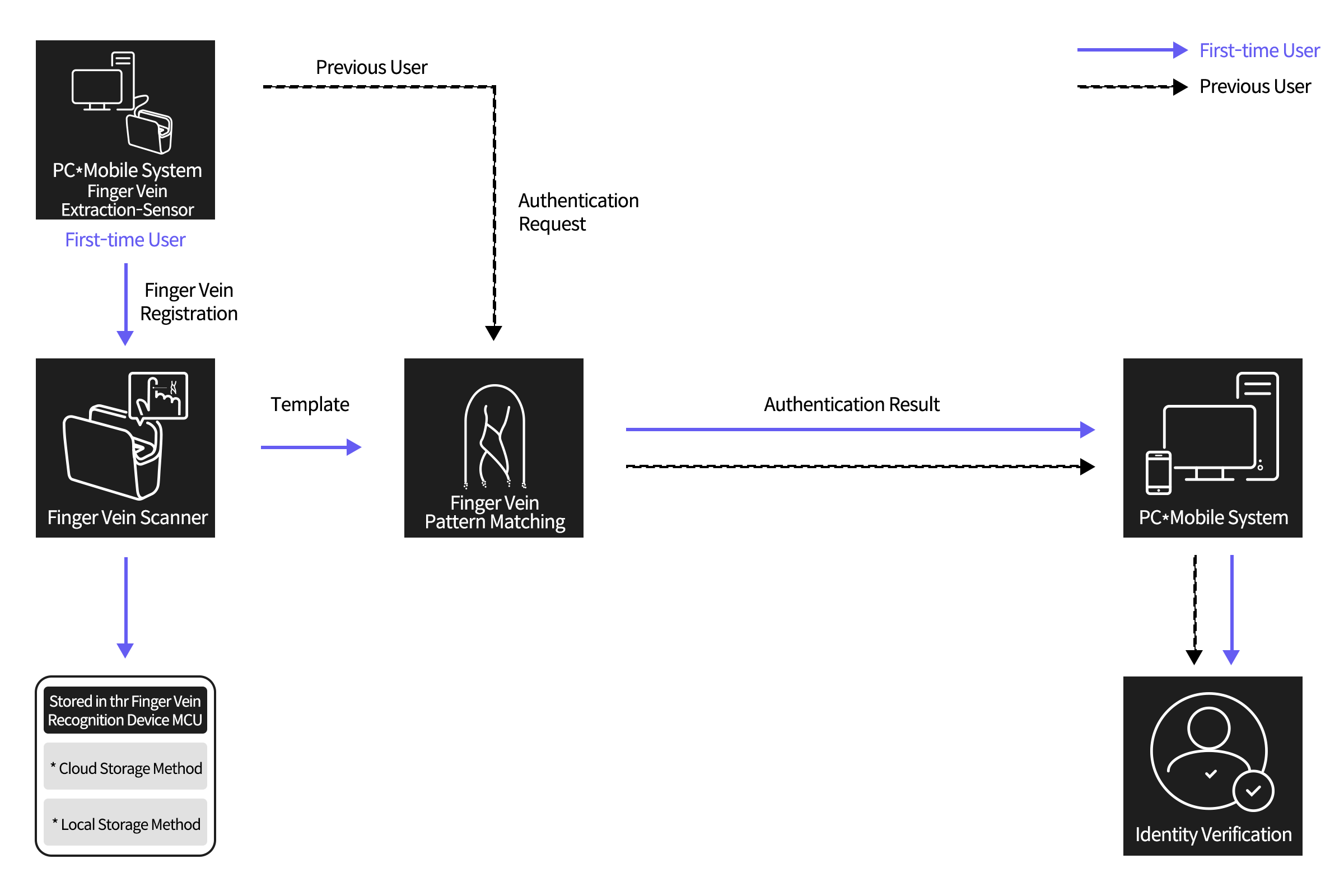
Authentication Process
[ The process of extracting Finger vein patterns and verifying them against stored Finger vein patterns for authentication ]